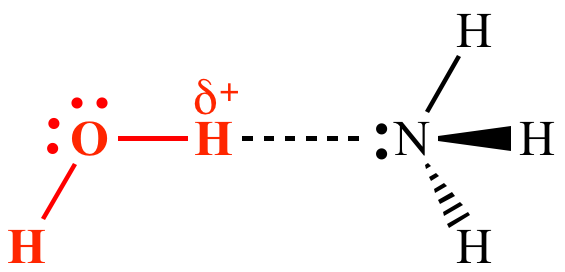Hydrogen Bond
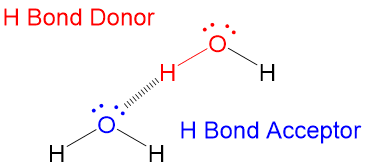
Hydrogen bonds occur when a hydrogen atom undergoes dipole dipole attractionto an electronegativeatom.
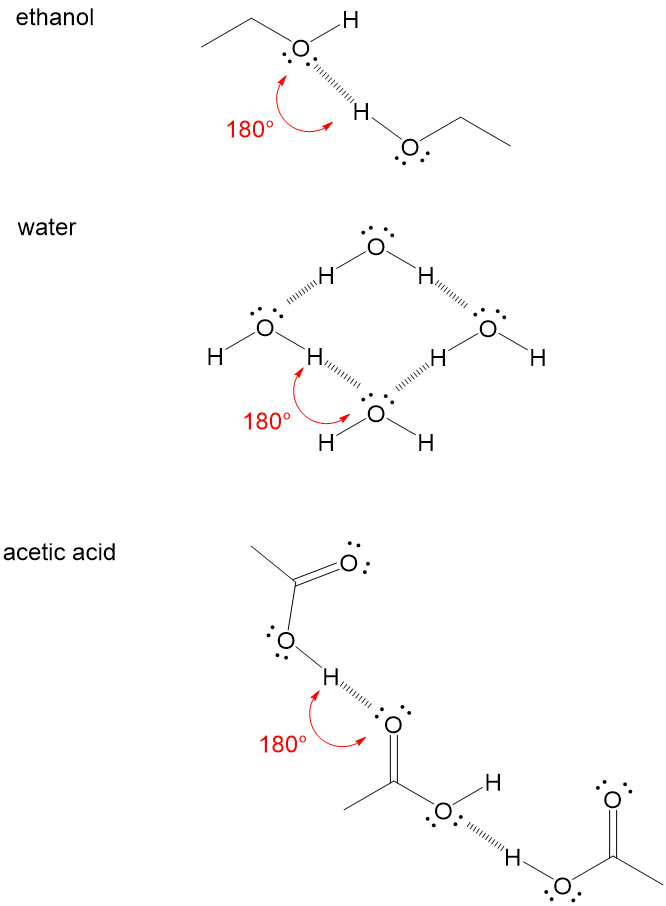
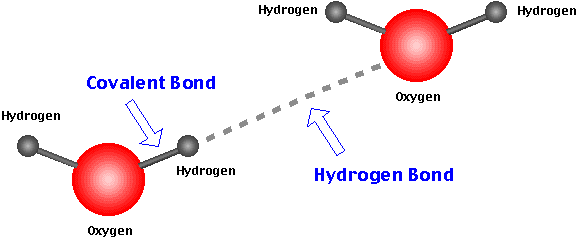
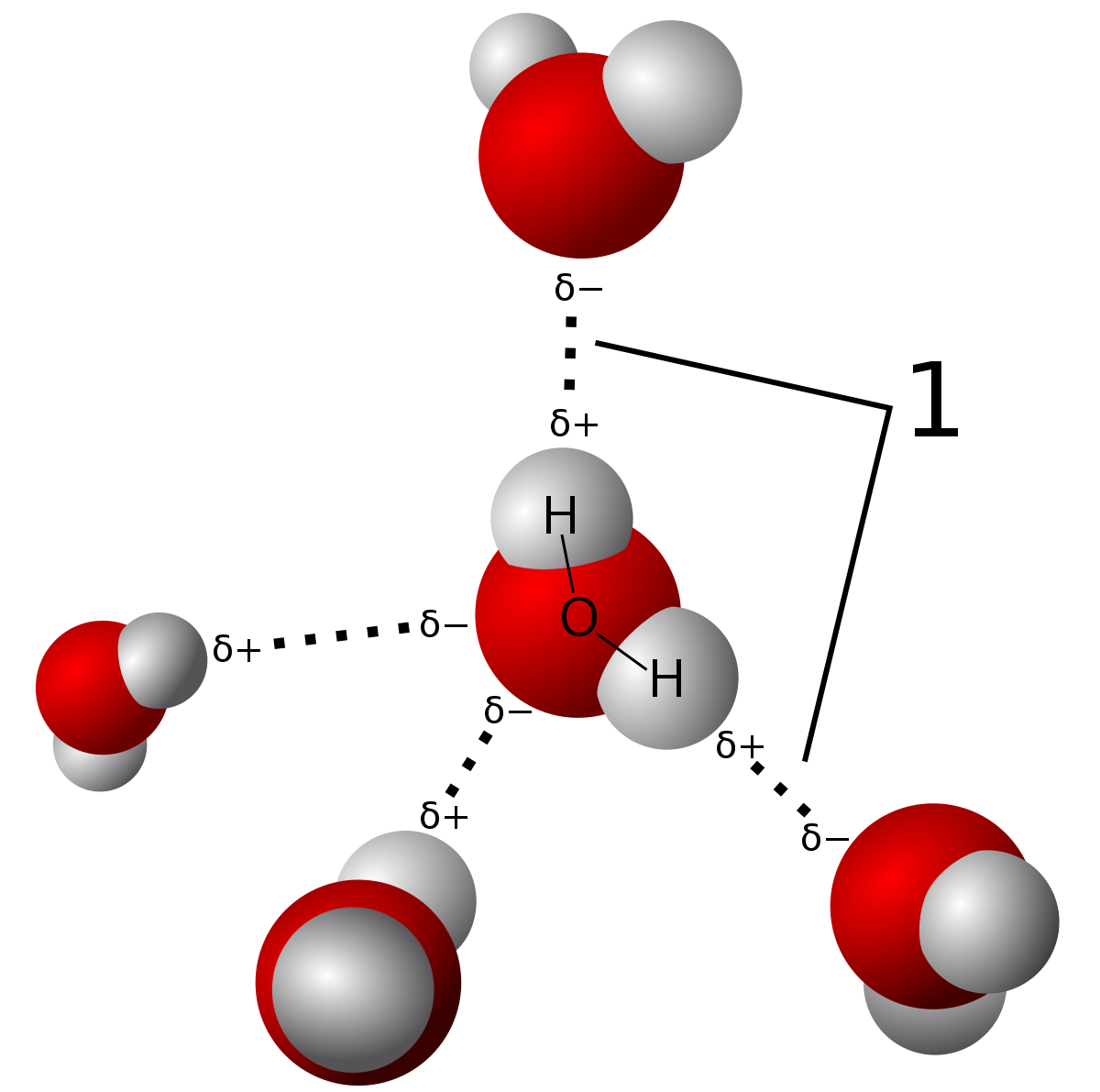
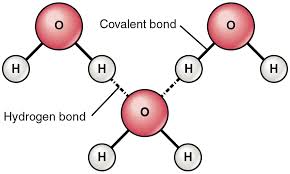
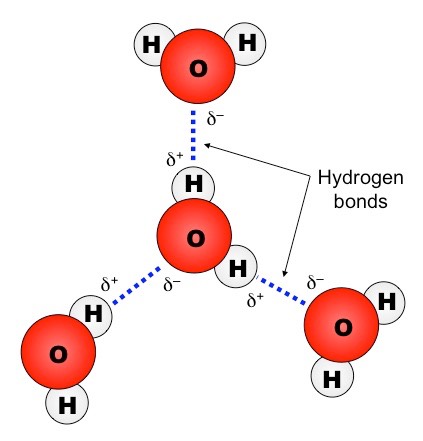
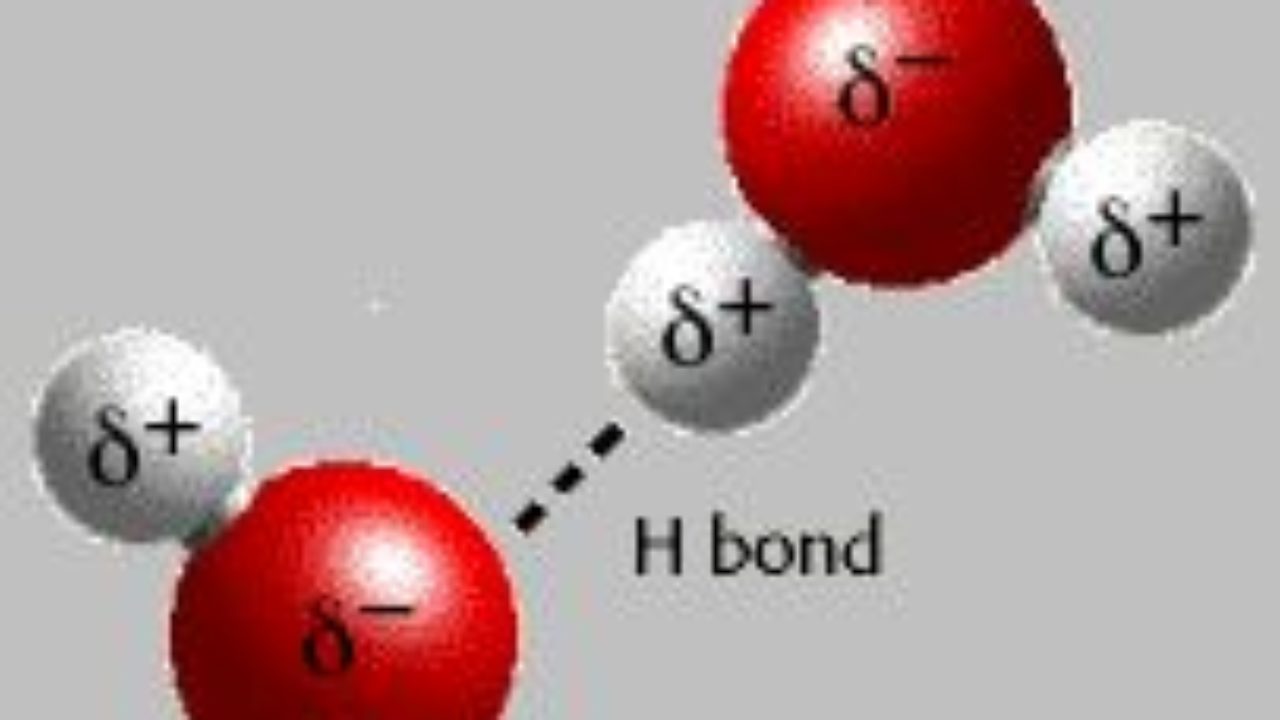
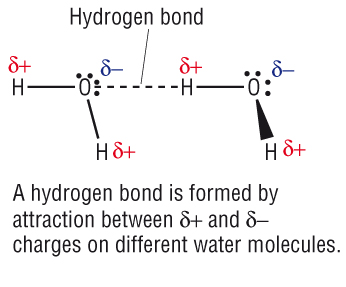
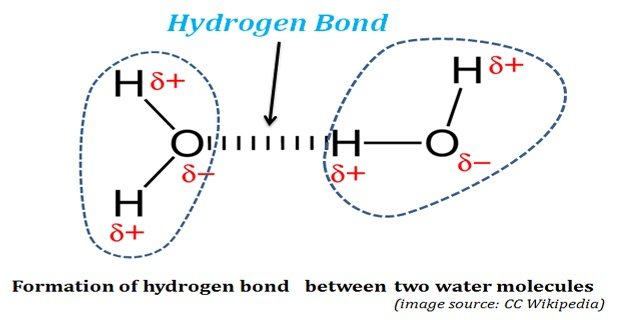
Hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonds may form between atoms within a molecule or between two separate molecules. Water molecules forming hydrogen bonds with one another. Differences in electronegativity between the hydrogen atom and the other atom or atoms of the molecule lead to these partial positive and partial negative charges. Water molecules are also attracted to other polar molecules and to ions.
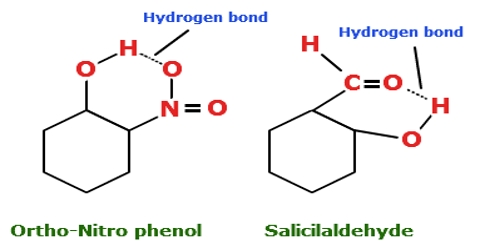
Hydrogen bonds can exist between atoms in different molecules or in parts of the same molecule. A hydrogen bond is an attraction between two atoms that already participate in other chemical bonds. Hydrogen forms covalent bonds with nonmetal atoms. Sometimes the bonding is intramolecular or between atoms of a molecule rather than between atoms of separate molecules intermolecular.
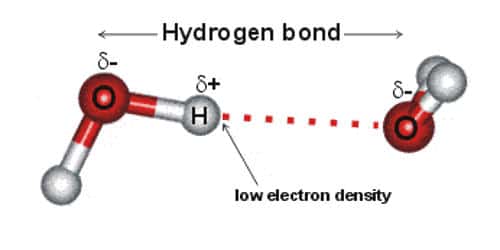
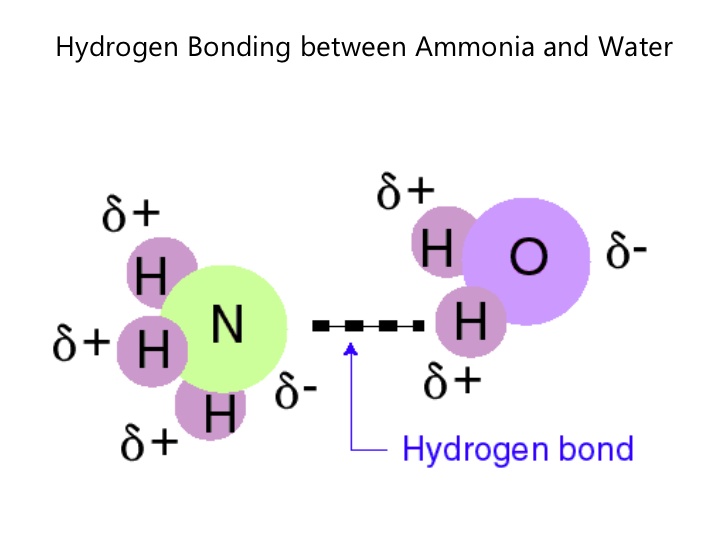
Hydrogen bonds form because of the attraction between a slightly positive hydrogen atom of one molecule and the slightly negative atom of another molecule. Hydrogen bonding is a special type of dipole dipole attraction betweenmolecules not a covalent bond to a hydrogen atom. Usually hydrogen bonds occur between hydrogenand fluorine oxygen or nitrogen. Hydrogen bonding interaction involving a hydrogen atom located between a pair of other atoms having a high affinity for electrons.
This means that the two atoms share electrons with one another. It results fromthe attractive force between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded toa very electronegative atom such as a n o or f atom and another veryelectronegative atom. Hydrogen bond strengths range from 4 kj to50 kj per mole of hydrogen bonds. This can happen either between different molecules as in intermolecular.
The partial negative charge on the o of one molecule can form a hydrogen bond with the partial positive charge on the hydrogens of other molecules. Such a bond is weaker than an ionic bond or covalent bond but stronger than van der waals forces. Hydrogen bonds are formed when the positive end of a polar molecule is attracted to the negative end of a polar molecule. Hydrogen bond definition is an electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom in one polar molecule as of water and a small electronegative atom as of oxygen nitrogen or fluorine in usually another molecule of the same or a different polar substance.
This is a very weak bond and strength of hydrogen bond 5 10 kcal per bond is much less than the strength of covalent bond.




















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/water-molecules-136810077-5c448a6ec9e77c0001568fb2.jpg)